Depth stratified light trap sampling reveals variation in the depth distribution of late-stage cryptobenthic reef fish larvae
Authors: Sophia Douglas, Sterling Tebbett, Severine Choukroun, Christopher Goatley & David Bellwood
Abstract:
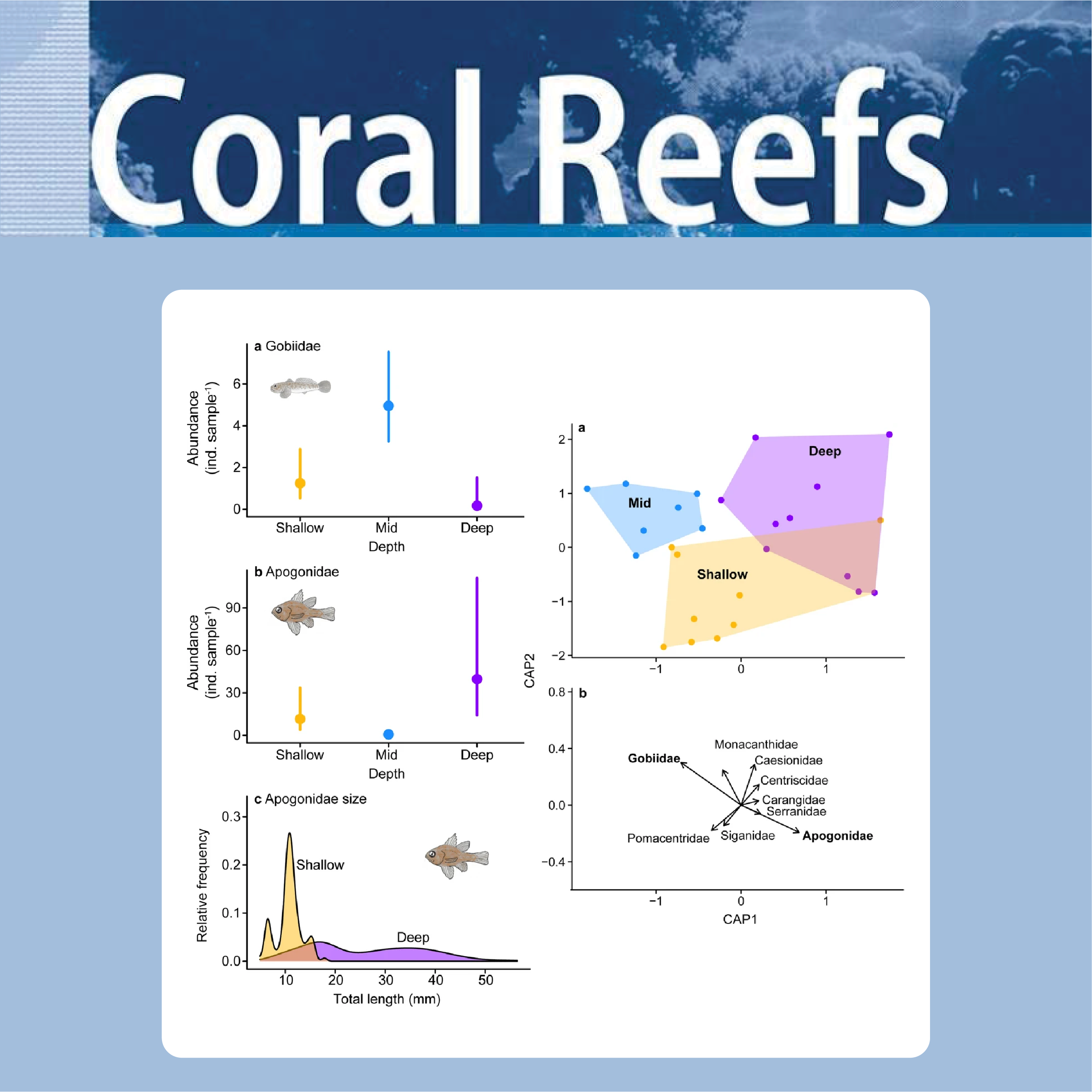
Cryptobenthic fishes are abundant on coral reefs, and their larvae dominate the ichthyoplankton in near reef waters. However, we have a limited understanding of how pelagic and on-reef processes are linked, especially how late-stage cryptobenthic fish larvae use near reef waters. We therefore used depth-stratified light trap sampling from 2 to 27 m at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. This revealed clear depth variation in late-stage larval fish assemblages. Gobiidae larvae characterised mid-depth (13 m) samples. By contrast, larval Apogonidae were only abundant in shallow samples. Deep samples were typified by (non-target) adult apogonids. Contrary to expectations that poor-swimming cryptobenthic larvae would be flow-sheltering in deeper water, our results suggest that late-stage cryptobenthic larvae use large portions of the water column, although their preferred positions may be taxon-specific.